Grain-Free Dog Food: Is It Right for Your Pet?

Key Takeaways
- Grain-free dog food may help dogs with digestive sensitivities, but it is not necessary for most, as grains are generally well-tolerated.
- Monitoring dogs on grain-free diets for health changes is important, with veterinary consultation advised regularly.
- Gradual transitions to grain-free food over a week help ensure balanced nutrition and reduce digestive issues.
Understanding Grain-Free Dog Food
Pet owners strive to provide dogs with the best care, from choosing sturdy toys to offering nutritious meals. Selecting the right food is a complex task as diets must suit a dog’s specific needs based on age, breed, and health status. Grain-free dog food has become very popular, using ingredients like peas, lentils, chickpeas, and sweet potatoes instead of grains such as wheat or rice.
PetHealthMD is a helpful resource for pet owners offering trusted insights on nutrition trends, ingredient safety, and more. Understanding your dog’s unique needs and working closely with your vet can help guide the best decision for their long-term health.
Benefits of Grain-Free Dog Food
Dogs have varied dietary needs shaped by genetics, activity levels, and health conditions. For some dogs, grain-free diets can provide targeted nutritional support that improves digestion, energy levels, and overall wellness. Choosing the right formula can make a significant difference in your dog’s comfort, appearance, and health.
Supports Sensitive Stomachs
- Uses alternative carbohydrates like sweet potatoes, lentils, or chickpeas.
- May ease bloating, loose stools, chronic gas, and general digestive discomfort.
- Provides steady, easily digestible energy for daily activities.
Enhances Energy and Muscle Maintenance
- Often includes higher protein levels suited for active breeds.
- Supports stamina, endurance, and recovery for energetic lifestyles.
Promotes a Healthy Coat and Skin
- Protein sources like salmon or lamb help maintain a glossy coat and healthy skin.
- Improves overall appearance and skin comfort.
Tailored Nutrition for Puppies and Growth
- Grain-free formulas are designed to support puppy development.
- Provide essential nutrients like calcium and balanced calories.
- Options available for calorie-dense diets or lower-calorie diets to manage a healthy weight.
Encourages Monitoring and Adjustment
- Nutritional science recommends tracking weight, digestion, and energy levels to assess diet effectiveness.
- Veterinary guidance ensures the diet adapts to the dog’s unique health needs over time.
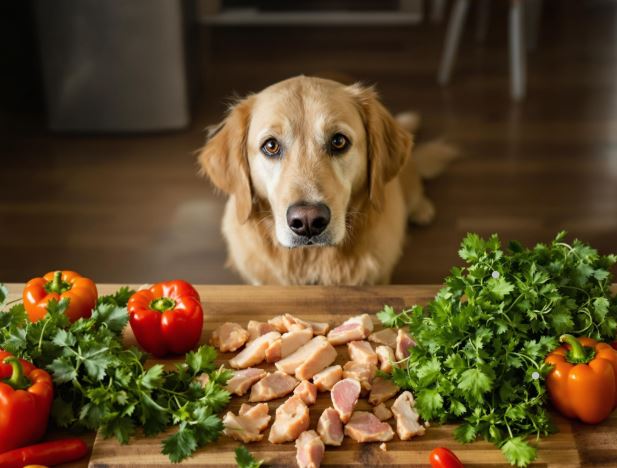

Grain-Free vs Regular Dog Food
Understanding the differences between grain-free and grain-inclusive dog food involves sorting through many options. Traditional dog foods use grains like rice, wheat, barley, or corn, which offer digestible energy and fiber. Most dogs handle grains well, gaining from their slow energy release. Grain-free formulas rely on peas, lentils, or sweet potatoes, providing similar energy with nutrient profiles suited to specific dietary needs.
True grain allergies are rare. Proteins like chicken or beef more commonly cause reactions. While grain-free diets are often promoted as natural, modern dogs digest starches well. Active dogs may do well with grain-inclusive diets for lasting energy, while less active or senior dogs might benefit from grain-free options for weight control.
Cost can be higher for grain-free foods since they include premium ingredients. Regardless of cost, high-quality foods meeting AAFCO standards ensure balanced nutrition.
To explore food and nutrition options, visit the Dog Food and Diet category on PetMeds.
Grain-Free Diets and Dilated Cardiomyopathy DCM
Grain-free diets provide benefits but carry risks that need attention. The FDA’s study on dilated cardiomyopathy connects many cases to grain-free foods, especially in breeds like Golden Retrievers. DCM weakens heart function, possibly due to low taurine levels in diets high in legumes or pulses.
Symptoms like fatigue, coughing, labored breathing, or fainting require immediate veterinary attention. Some pet owners mix grain-free with grain-inclusive diets or choose formulas with added taurine. Regular veterinary visits, including heart screenings for at-risk breeds, are essential.
How to Transition to Grain-Free Dog Food Safely
Switching to grain-free dog food requires a slow process to prevent digestive problems. Veterinarians should review a dog’s health and diet history to ensure the switch is suitable. A 7 to 10 day transition lowers the risks of gas or diarrhea.
Feeding Transition Schedule
Days 1 to 2: 1/2 cup grain-free with 1 1/2 cups regular food
Days 3 to 4: 1 cup grain-free with 1 cup regular food
Days 5 to 6: 1 1/2 cups grain-free with 1/2 cup regular food
Day 7 onward: 2 cups grain-free food
Signs of a smooth transition include firm stools, steady energy, and a glossy coat. Vomiting or tiredness requires stopping the switch and consulting a veterinarian. Sensitive dogs may need a 14-day transition or probiotics.
Common Questions About Grain-Free Dog Food
What is grain-free dog food
It excludes traditional grains and uses peas, lentils, or sweet potatoes. These formulas often contain more protein and different fiber types.
Is grain-free food always healthier
Not always. Unless a dog has a confirmed grain allergy, whole grains can be beneficial.
Why are grain-free diets linked to heart disease
The FDA has investigated potential ties between grain-free diets and DCM, especially in foods with high legume content.
What signs show a dog might benefit from grain-free food
Chronic itching ear infections or digestive issues may indicate food sensitivities.
Should I consult a vet before switching diets
A vet can determine whether a diet trial is needed and help choose a balanced formula.
Is grain-free right for every dog
Many dogs do well on grain-inclusive diets. Grain-free may help dogs with specific sensitivities.
What benefits might grain-free offer
When appropriate, grain-free diets may reduce digestive problems and itching.
What should be monitored during a grain-free diet
Watch for fatigue, reduced activity, and discuss heart health with your vet.
What should I ask my vet before switching diets
Ask about nutrient needs, taurine monitoring, and complete and balanced guidelines.
Make the Best Dietary Decision for Your Dog
Choosing your dog’s diet means matching nutrition to their individual needs. Grain-free diets may help with sensitivities, but possible heart risks call for caution. Focus on food quality, your dog’s response, and regular checkups.
To explore nutrition products, visit the Dog Food and Diet category.